Understanding Laneway Houses
Laneway houses are secondary dwelling units built on the same property as a primary residence, typically accessed from a laneway or alleyway. These homes offer a unique blend of urban living and privacy, providing a distinct alternative to traditional housing options.
Laneway houses have gained popularity due to their numerous advantages, particularly for families or individuals seeking additional living space. These benefits can range from generating rental income to providing accommodation for aging parents or adult children.
Regulations and Zoning Requirements, 2 bedroom laneway house plans
The construction and legality of laneway houses vary significantly across different regions. Understanding the specific regulations and zoning requirements is crucial before embarking on any laneway house project.
Local governments often have specific guidelines regarding:
- Lot size and dimensions: Minimum lot sizes and setbacks from property lines are commonly stipulated to ensure adequate space and privacy for both the primary and secondary dwelling units.
- Building codes and standards: Laneway houses must adhere to building codes and safety standards, similar to those for primary residences. This includes requirements for fire safety, structural integrity, and accessibility.
- Parking requirements: Regulations may specify the number of parking spaces required for both the primary and laneway houses, which can vary depending on the location and density of the neighborhood.
- Utilities and services: Connecting the laneway house to utilities such as water, sewer, electricity, and gas may require permits and adherence to specific regulations.
It is essential to consult with local authorities and obtain the necessary permits before commencing any construction.
Designing a 2-Bedroom Laneway House: 2 Bedroom Laneway House Plans

Designing a 2-bedroom laneway house involves balancing functionality, aesthetics, and efficient space utilization. This guide explores various design considerations, floor plan examples, and sustainable construction practices to help you create a comfortable and functional living space within a compact footprint.
Floor Plan Considerations
Floor plan layout is crucial in maximizing space and functionality in a 2-bedroom laneway house. Different layout options offer unique advantages and disadvantages, impacting the flow of traffic, natural light, and overall living experience.
- Open-Concept Layout: This design promotes a sense of spaciousness by combining living, dining, and kitchen areas. This layout is ideal for maximizing natural light and creating a social atmosphere. However, it can lead to noise carryover and a lack of privacy.
- Closed-Off Layout: This design emphasizes privacy and separation by creating distinct rooms for each function. This layout provides better sound insulation and individual space, but it can feel cramped and limit natural light penetration.
- Split-Level Layout: This design utilizes different levels to create a sense of space and separate living areas. A split-level layout can accommodate different room functions, such as a bedroom on the lower level and a living area on the upper level. This design offers privacy and visual interest, but it can require careful planning to ensure proper flow and access.
Space Optimization Techniques
Optimizing space is essential in a laneway house, as every square foot counts. Incorporating strategic design elements can enhance functionality and create a sense of spaciousness.
- Built-in Storage: Utilize built-in shelves, cabinets, and closets to maximize vertical space and minimize clutter. This approach maximizes usable floor area and provides a streamlined aesthetic.
- Multifunctional Furniture: Opt for furniture that serves multiple purposes, such as a sofa bed or a dining table that doubles as a workspace. This approach maximizes flexibility and minimizes the need for dedicated furniture pieces.
- Compact Appliances: Choose compact appliances, such as a smaller refrigerator or a combination washer-dryer, to save space without sacrificing functionality. This approach is particularly relevant in kitchens and laundry areas.
Sustainable Design Features
Integrating sustainable design features into a laneway house construction can minimize environmental impact and reduce energy consumption.
- Energy-Efficient Windows: Install double- or triple-paned windows with low-e coatings to improve insulation and reduce heat loss. This approach minimizes reliance on heating and cooling systems.
- Solar Panels: Consider installing solar panels to generate clean energy and reduce reliance on the grid. This approach can significantly reduce energy bills and contribute to a sustainable lifestyle.
- Green Building Materials: Utilize eco-friendly building materials, such as bamboo, recycled wood, or sustainably sourced lumber, to minimize environmental impact. These materials are often durable and aesthetically pleasing.
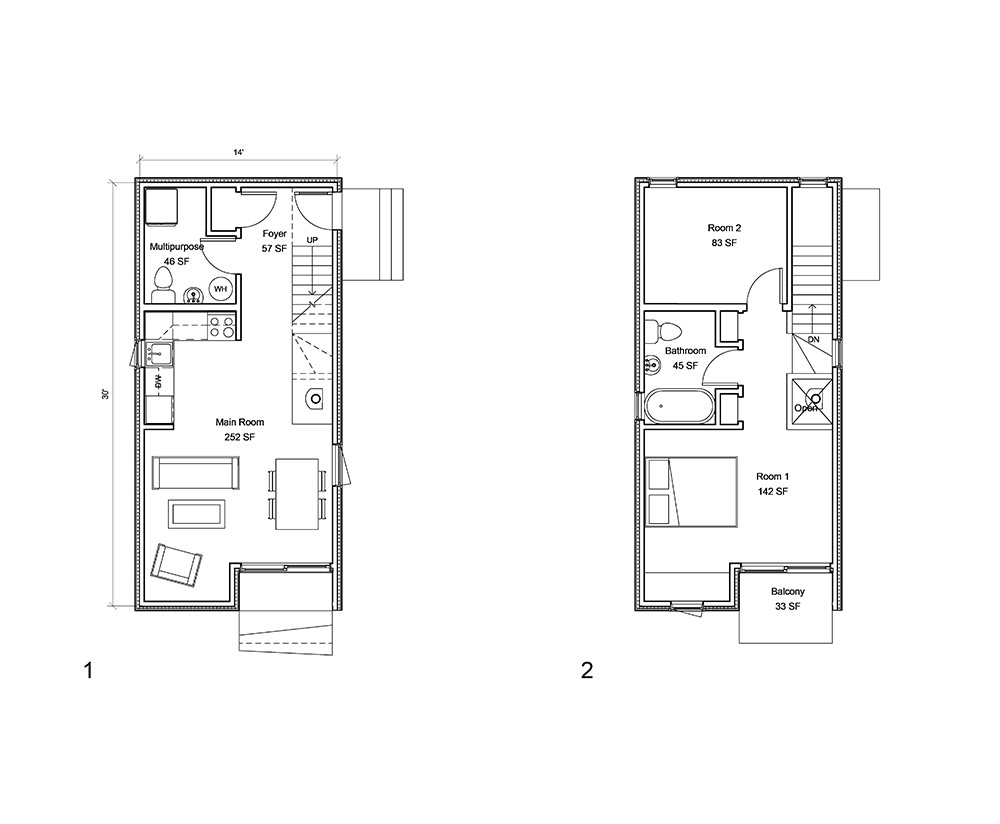
Examples of 2-Bedroom Laneway House Floor Plans
- Plan A: This plan features an open-concept living area with a kitchen, dining, and living room combined. Two bedrooms are located at the rear of the house, with a shared bathroom in the middle. This layout offers a spacious living area and ample natural light.
- Plan B: This plan features a more traditional layout with separate rooms for each function. The living room is located at the front of the house, followed by the kitchen and dining area. The two bedrooms are situated at the rear, each with its own bathroom. This layout provides greater privacy and sound insulation.
- Plan C: This plan utilizes a split-level design, with the living room and kitchen located on the upper level and the bedrooms on the lower level. This layout offers a sense of space and separation, with the bedrooms enjoying privacy and natural light from a lower level.
Construction Considerations for 2-Bedroom Laneway Houses

Building a 2-bedroom laneway house is a significant undertaking, requiring careful planning, meticulous execution, and adherence to local regulations. This section delves into the key steps involved in constructing a laneway house, from the initial planning and permitting phases to the final construction and finishing touches. It also explores the diverse construction materials and techniques commonly employed in laneway house building, and provides an overview of the associated costs, encompassing labor, materials, and permits.
Planning and Permitting
The initial phase of constructing a laneway house involves comprehensive planning and obtaining the necessary permits. This crucial step ensures that the project aligns with local building codes and zoning regulations.
- Site Assessment: This involves evaluating the site’s suitability for a laneway house, considering factors such as lot size, access, utilities, and soil conditions.
- Design Development: A detailed design plan is crucial, encompassing the floor plan, elevations, and structural details. This plan must comply with local building codes and zoning regulations.
- Permit Applications: Submitting a complete set of plans and documentation to the relevant authorities is necessary to obtain the required building permits. This process typically involves multiple inspections and approvals.
Construction Materials and Techniques
The selection of construction materials and techniques plays a significant role in the overall cost, durability, and aesthetic appeal of a laneway house.
- Foundation: Common foundation types include concrete slabs, crawl spaces, and basements. The choice depends on site conditions, budget, and local regulations.
- Framing: Wood framing is the most prevalent technique for laneway houses. Steel framing offers advantages in terms of fire resistance and durability but is typically more expensive.
- Exterior Cladding: Options include wood siding, brick, stone, stucco, and fiber cement. The choice depends on aesthetic preferences, budget, and maintenance requirements.
- Roofing: Shingles, metal roofing, and flat roofs are commonly used. The choice depends on factors such as climate, aesthetics, and budget.
Construction Costs
The cost of constructing a 2-bedroom laneway house varies considerably depending on factors such as location, materials, and design complexity.
- Labor Costs: Labor costs account for a significant portion of the overall budget, typically ranging from 25% to 40% of the total construction cost. Skilled labor is essential for framing, plumbing, electrical, and finishing work.
- Material Costs: Material costs vary widely depending on the chosen materials. High-quality materials often come with a higher price tag but can provide long-term durability and aesthetic appeal.
- Permit Fees: Permit fees vary by jurisdiction and can range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars, depending on the size and complexity of the project.
- Other Costs: Other costs to consider include landscaping, utilities, and furniture.